Earthquakes can feel scary, but they are a natural part of how our planet works, and this topic is popular because scientists around the world study earthquakes to keep people safe.
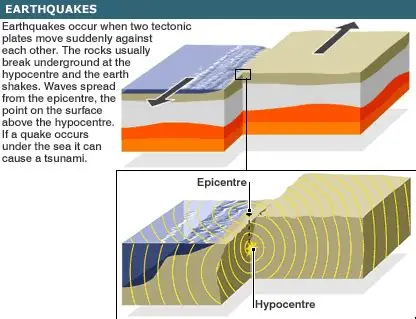
An earthquake happens when the ground suddenly shakes because of movements deep inside the Earth. These movements release energy that travels as waves through the ground.
What causes earthquakes
The Earth’s outer layer is broken into large pieces called tectonic plates. These plates:
-
Move very slowly
-
Push against each other
-
Sometimes get stuck
When the pressure becomes too strong, the plates suddenly move — and that causes an earthquake.
Where do earthquakes happen most
Earthquakes happen more often:
-
Near plate boundaries
-
Along fault lines
-
Around oceans and mountains
Countries like Japan, Indonesia, Chile and parts of India experience earthquakes more often because they are near active plate edges.
How earthquakes are measured
Scientists use a tool called a seismograph to measure earthquakes. The strength is measured using a scale called magnitude.
-
Small earthquakes may not be felt
-
Strong earthquakes can damage buildings
Scientists cannot stop earthquakes, but they work hard to predict risks and give safety advice.
What to do during an earthquake
Experts advise:
-
Stay calm
-
Drop to the ground
-
Take cover under a table
-
Hold on until shaking stops
Schools often conduct earthquake drills so children know how to stay safe.
Why kids should care
-
Earthquakes teach us how Earth works
-
Safety knowledge can save lives
-
Science helps reduce fear
Teachers say learning about earthquakes builds awareness, preparedness and respect for nature’s power.
Scientists are also using satellites and AI to study ground movements and improve early warning systems.
In short: Earthquakes happen when tectonic plates move and release energy, causing the ground to shake.
Learning takeaway: Understanding earthquakes helps us stay prepared, calm and safe when nature shows its strength. 🌎🧠