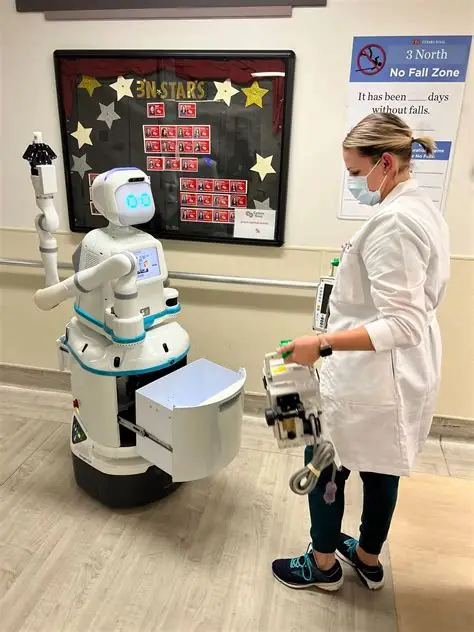
Hospitals in several countries are beginning to use robots to help doctors and nurses, making this a trending and exciting technology story. Health experts say these robots are not replacing people but are designed to support medical staff by doing simple, repetitive, or risky tasks, allowing doctors and nurses to spend more time caring for patients.
Some hospital robots are used to deliver medicines, meals, and medical supplies from one room to another. Others help clean hospital floors and rooms using special lights and disinfectants that kill germs. By doing these jobs, robots help reduce the spread of infections and keep hospitals safer for everyone.
Doctors also use robots in surgeries, where machines help make very precise movements. These surgical robots are controlled by trained surgeons and can assist with delicate operations. Experts say this can help reduce recovery time for patients and improve accuracy during procedures.
The use of robots in hospitals has grown because of advances in artificial intelligence and engineering. These machines can follow instructions, avoid obstacles, and work for long hours without getting tired. Hospital staff say robots are especially useful during busy times, such as during flu seasons or emergencies.
For kids, this news is important because it shows how science and technology can be used to help people. Robots are not just for factories or movies; they can also play a role in keeping people healthy. Learning about robotics may inspire students to explore careers in science, medicine, or engineering.
Experts remind everyone that kindness, care, and human judgment are still the most important parts of healthcare. Robots are tools that assist people, not replace them. Doctors and nurses continue to make all important decisions and provide comfort and support to patients.
The growing use of robots in hospitals highlights how technology is changing everyday life in helpful ways. As research continues, these smart machines may become even better at supporting healthcare workers and improving care for patients around the world.