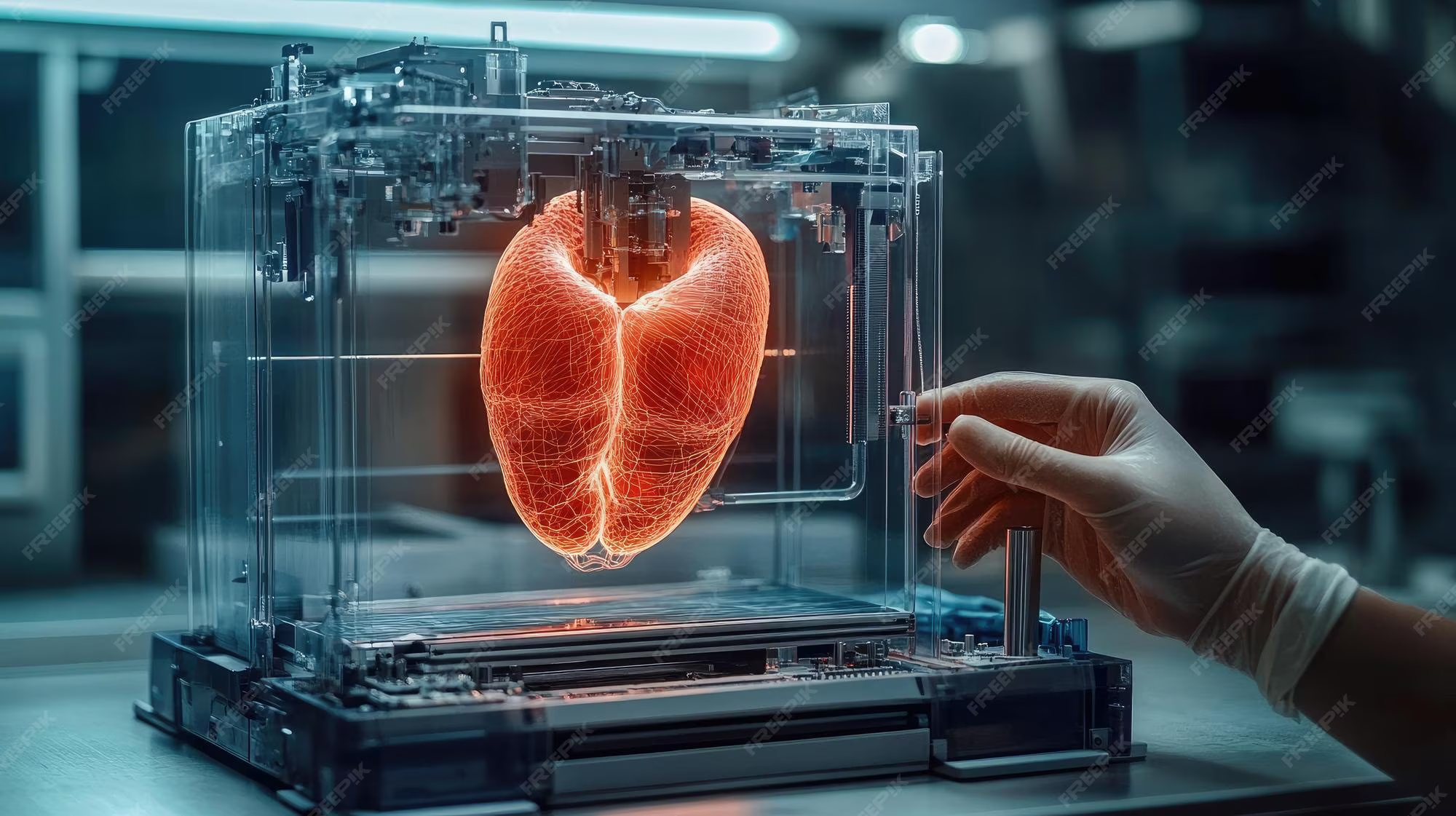
Scientists and medical researchers are exploring 3D bioprinting technology to develop artificial organs, making this an important health and medical innovation news story for children. 3D bioprinting is a process where living cells are used as “ink” to print tissue structures layer by layer.
Organ failure affects many people worldwide. Doctors explain that sometimes patients must wait a long time for organ transplants. Bioprinting technology aims to create tissues that could one day replace damaged organs.
In a laboratory, scientists use special printers to place living cells in precise patterns. These cells grow and form tissue structures. Researchers are currently focusing on printing simple tissues such as skin and cartilage.
For children, this news matters because medical innovation improves healthcare and saves lives. Advances in technology may help doctors treat patients more effectively in the future.
Bioprinting is still in the research stage. Experts say printing complex organs like hearts or kidneys is challenging because they require detailed blood vessel systems.
Scientists test bioprinted tissues carefully to ensure safety and functionality.
Schools teach students about biotechnology and medical science to inspire future healthcare careers.
Researchers collaborate globally to improve printing materials and cell growth techniques.
Ethical guidelines ensure that medical research follows strict safety standards.
The development of bioprinting shows how science and medicine work together to address health challenges.
Learning about medical innovation teaches children how technology can support human wellbeing.
By advancing 3D bioprinting research, scientists hope to create new treatment possibilities that improve patient care worldwide.