Wildlife scientists are tracking migratory birds to better understand climate change, making this an important wildlife and biodiversity news story for children. Migratory birds travel long distances each year between breeding and wintering grounds, and their journeys provide valuable scientific information.
Bird migration is guided by natural instincts and environmental cues. Scientists explain that birds use the position of the sun, stars, and even Earth’s magnetic field to navigate across continents.
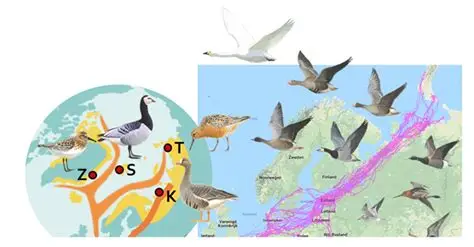
Researchers attach small tracking devices to certain birds to study their routes. These devices send signals to satellites, allowing scientists to map migration paths and study timing changes.
For children, this news matters because bird migration shows how closely animals are connected to seasonal changes. If temperatures rise or habitats disappear, migration patterns can shift.
Experts have observed that some bird species are arriving earlier at breeding grounds due to warmer springs. These changes may affect food availability and nesting success.
Studying migratory birds also helps scientists protect important habitats such as wetlands and forests.
Schools teach students about migration through geography and science lessons. Birdwatching activities help children appreciate wildlife.
Conservation organizations work to protect stopover sites where birds rest during long journeys.
Scientists emphasize the importance of reducing pollution and protecting natural ecosystems to support bird populations.
Tracking migration patterns provides insight into global environmental changes.
The study of migratory birds demonstrates how wildlife research contributes to climate science.
Learning about bird migration teaches children the importance of biodiversity and environmental stewardship.
By understanding migration patterns, scientists can better protect ecosystems and ensure that future generations continue to witness the wonder of bird journeys across the skies.